Starting in April 2020, Yodlee began rolling out a new, simpler authorization method compliant with the OAuth 2 framework. The new approach offers a Client Credential grant type, which we'll refer to as CC for short. Previously Yodlee required a JSON Web Token (JWT) based approach, along with other legacy techniques. Authorization with CC tokens is much simpler and quicker than using JWTs. You don’t have to mint an authentication token using cryptography, as you do with JWTs. You get a CC token by making an API call to request one.
Users who created accounts after April 2nd 2020 have already had access to CC. As of August 27th, users signed up to our Sandbox tier service only have been migrated to CC. We will announce further migrations and the eventual end-of-life of JWT authorization for remaining customers in upcoming months.
This post will guide Yodlee developers using JWTs migrating to CC. Not sure if this applies? Login to your developer account and look at the dashboard page. If you have two tabs at the top labeled "Client Credentials" and "JWT", this post is for you.
Calendar for moving Sandbox developers from JWT to CC
Yodlee wants all developers in the developer portal to switch from JWT authentication to CC token authentication. We’re encouraging Sandbox environment users to switch first, allowing a period of about one month to adopt CC tokens. After all sandbox users are moved to CC tokens, we will coordinate with users who are using JWTs in development and/or production environments, to help you adopt CC tokens. The adoption time period for development and production will be much longer than one month, and we will provide further guidance in due course.
Process for moving Sandbox developers to CC
Developers are issued their JWT credentials on their developer account. We are adding a set of CC credentials to the account of every JWT user in the sandbox. The CC credentials consist of two strings, called a “client ID” and a “client secret”, and they look like this:
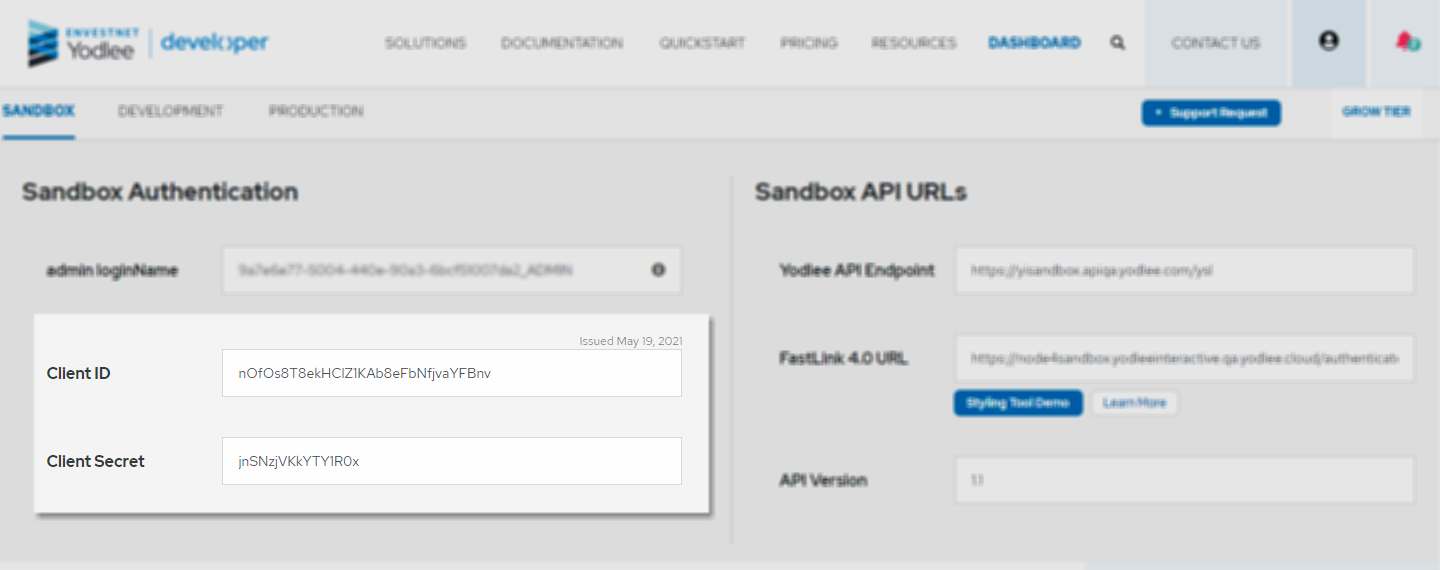
You should keep both of these strings confidential because they control your access to the Yodlee servers. If your credentials are compromised, your developer dashboard offers a way to request replacements (for live environments only, not in the sandbox).
How to get a CC token
You get a CC token by making an API call to ask the Yodlee API server to give you one. You will pass three data items in your POST /auth/token request:
1. Your client ID. This should be URL encoded and passed in the HTTP request body.
2. Your client secret. This should also be URL encoded and passed in the http request body.
3. The login name of the user whose data you want to work with on subsequent API calls. The login name is a unique identifier for your end-users. You are given five end-user login names for use in the sandbox. In live environments, you will assign the unique identifiers for your users.
A brief note about encoding. The post body for a token request must be URL form encoded. Since the characters for the client ID and secret don't require any modification to fit this scheme, in reality this has little impact on your code. Just make sure to specify a Content-Type header of application/x-www-form-urlencoded. Many libraries will do this for you. See the section on URL form encoding here for more information.
Test your new CC credentials
Now test your CC token. Follow the Quickstart trail, and use the Postman API-calling application. The steps are listed in Flow 1, "Step 1 Authenticate" on Quickstart. Once you have your CC token, you pass it as the "Authorization: Bearer” HTTP header in subsequent API calls, exactly like you do with a JWT token.
We think you will like the simplicity and speed of implementation of CC tokens.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers.
Q1. What do I do if I’m using the prior authentication, cobrand login?
A. Cobrand logins will be addressed in the next phase of this transition.
Q2. What happens if I don’t migrate to use CC?
A. We plan to turn off JWT support in the sandbox 30 days after announcing the migration program. You won’t be able to make API calls in the sandbox using JWTs after that time. You’ll be able to move to one of the live environments, and changeover to use CC tokens there.
Q3. Is CC more secure than JWT?
A. Security experts regard the two kinds of token as about equal in terms of high security.
Q4. For developers currently using JWTs in a live environment, what is their path to use CCs?
A. This will be handled in the second phase of migrations, which only starts, after all, sandbox JWT developers are moved to CC. There will be a much longer grace period for taking up CC credentials because you will have to update the code you have running.
----
Photo by marcos mayer on Unsplash
